Hexaazatriphenylene derivatives/GO composites as organic cathodes for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
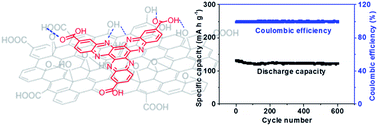
Redox active organic molecules as cathode materials for lithium ion batteries are promising. However, these compounds are plagued by their high solubilities in electrolyte solution, leading to capacity decay and a short cycling life. Herein, we report nano-composites of hexaazatriphenylene (HAT) derivatives and graphene oxide (GO) (hexaazatrinaphthalene (HATN)/GO and hexaazatrinaphthalene tricarboxylic acid (HATNTA)/GO) as cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. HAT derivatives demonstrate strong π–π and H-bond interactions with GO, which remarkably suppress their dissolution in electrolyte, leading to significant improvement of their electrochemical performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...