Computational investigation of microgels: synthesis and effect of the microstructure on the deswelling behavior†
Abstract
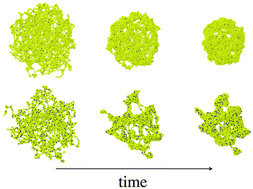
We present computer simulations of a realistic model of microgels. Unlike the regular network frameworks usually assumed in the simulation literature, we model and simulate a realistic and efficient synthesis route, mimicking cross-linking of functionalized chains inside a cavity. This model is inspired, e.g., by microfluidic fabrication of microgels from macromolecular precursors and is different from standard polymerization routes. The assembly of the chains is mediated by a low fraction of interchain crosslinks. The microgels are polydisperse in size and shape but globally spherical objects. In order to deeply understand the microgel structure and eventually improve the synthesis protocol we characterize their conformational properties and deswelling kinetics, and compare them with the results found for microgels obtained via underlying regular (diamond-like) structures. For the same molecular weight, monomer concentration and effective degree of cross-linking, the specific microstructure of the microgel has no significant effect on the locus of the volume phase transition (VPT). However, it strongly affects the deswelling kinetics, as revealed by a consistent analysis of the domain growth during the microgel collapse. Though both the disordered and the regular networks exhibit a similar early growth of the domains, an acceleration is observed in the regular network at the late stage of the collapse. Similar trends are found for the dynamic correlations coupled to the domain growth. As a consequence, the fast late processes for the domain growth and the dynamic correlations in the regular network are compensated, and the dynamic correlations follow a power-law dependence on the growing length scale that is independent of the microgel microstructure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...