Abstract
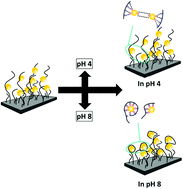
Doping polymer brushes with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) results in composite materials with colorimetric sensor properties. The present paper addresses the effect of electrostatic particle–particle interaction and the effect of the polymer brush type on particle assembly formation within the polymer matrix. The prospect for long-term use as colorimetric sensors is tested. Therefore, two different types of brushes of pH-insensitive polymers, non-ionic poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) and cationic poly-[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] trimethylammonium chloride (PMETAC), are studied. After incubation of the non-ionic PNIPAM brush in an aqueous suspension of AuNPs with a pH-sensitive carboxylic acid capping, hydrogen binding led to attachment of the AuNPs, but they were easily detached at high pH due to loss of the hydrogen binding. In contrast, the anionic AuNPs adhere well to cationic PMETAC brushes even after post-treatment at low pH where the charge density of the AuNPs is strongly reduced. Therefore, the PMETAC/AuNP composites were further tested with respect to their stability against pH variations and their impact for colorimetric sensors. Although the neat PMETAC brush is not pH-sensitive, after embedding pH-sensitive AuNPs, the PMETAC/AuNP composite becomes pH-sensitive in a reversible manner. This is detectable by the reversible shift of the plasmon band and the reversible thickness change of the composites by exposing them to different pH.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Electrostatics and Soft Matter


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...