Reversible-addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) mediated depolymerization of brush polymers†
Abstract
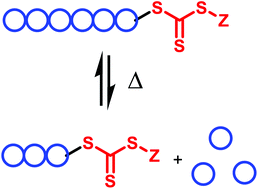
Brush polymers synthesized by reversible-addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization underwent depolymerization when heated in the absence of initiator. The depolymerizations followed pseudo first order kinetics and reached significant monomer concentrations (ca. 30 mM). RAFT polymerizations confirmed that depolymerizations reached thermodynamic equilibrium and the thermodynamic parameters of polymerization were independent of macromonomer molecular weight. Depolymerized polymers still had active terminal RAFT agents that could reinitiate polymerization, confirming that depolymerization was thermodynamically driven and mediated by the RAFT agent.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
