Mesoporous activated carbon from polyethyleneterephthalate (PET) waste: pollutant adsorption in aqueous solution
Abstract
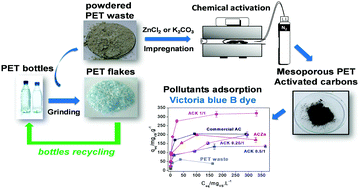
Mesoporous activated carbons (ACs) of high surface area were prepared from low cost and highly available powdered PET waste (generated during PET bottle recycling). Different chemical activating agents were employed. ZnCl2 produced an AC of 700 m2 g−1, containing mainly small mesopores (≈2 nm), whereas activation with K2CO3 produced carbons with larger mesopores (≈4 nm) and high BET surface area (up to ≈1400 m2 g−1). The investigation of the weight impregnation ratio of K2CO3/PET waste (1/1, 0.5/1 and 0.25/1) revealed that 1/1 generates the largest amount of mesopores (83%) besides high BET surface area (1210 m2 g−1). These ACs were used as adsorbents for the methylene blue (MB) and victoria blue B (VB) dyes in order to evaluate the potential adsorption of organic contaminants of different molecular sizes from water. The MB adsorption was mainly dependent on the ACs’ surface area, regardless of their pore size. The ACK 0.5/1 presented the highest MB adsorption capacity (625 mg g−1), considerably higher than that of a commercial AC (303 mg g−1). On the other hand, the highest adsorption amount of the bulky pollutant VB was obtained for the ACK 1/1 (323 mg g−1), possibly due to its higher mesoporosity and the presence of large mesopores of ≈4 nm size. These findings demonstrate the potential application of PET waste to produce value added products, such as activated carbons, for adsorption of organic contaminants from water, including relatively large pollutants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...