The construction of an electrochemical sensing interface based on nano-CeO2 cubes for highly sensitive detection of bisphenol A†
Abstract
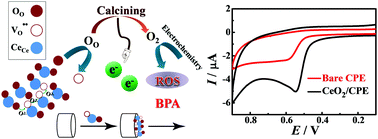
Nanocubic fluorite type CeO2 was synthesized via a hydrothermal & calcination strategy and was further characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). As for the unique oxygen vacancy structure of CeO2, the as-synthesized CeO2 nanocubes were utilized to establish a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for the determination of bisphenol A (BPA). The electrochemical performance of the CeO2 modified CPE, simplified as CeO2/CPE, was verified by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). The experimental results indicated that the conductivity and the electrocatalytic properties for BPA were enhanced significantly after the introduction of nanocubic fluorite type CeO2 due to the increased current density, promoted oxygen diffusion and increased amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) during the electrocatalytic process. According to the results of DPV, a good linear response was obtained for the determination of BPA in the concentration ranges of 0.01–5.97 and 5.97–49.57 μM with a detection limit of 0.003 μM (S/N = 3). The fabricated sensor also showed satisfactory stability, reproducibility, repeatability and anti-interference performance. Moreover, the CeO2/CPE showed excellent applicability and reliability in a practical sample analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...