Determination of baclofen and vigabatrin by microchip electrophoresis with fluorescence detection: application of field-enhanced sample stacking and dynamic pH junction†
Abstract
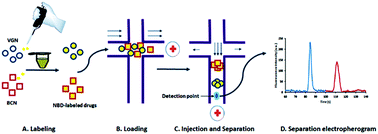
A simple, rapid and sensitive microchip electrophoretic (MCE) method with fluorescence detection is described for the simultaneous determination of two GABA analogue drugs, baclofen (BCN) and vigabatrin (VGN). Pre-microchip derivatization of both analytes with 4-fluoro-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole (NBD-F) was performed in a basic borate buffer. The NBD-fluorescent derivatives of the studied drugs (λex/em 470/540) were baseline separated in a dynamically-coated poly(methyl methacrylate) microfluidic channel within 120 s using a 40 mM borate buffer containing 0.4% methylcellulose as the background solution. The ability of methylcellulose to form a network sieve of small pore size allowed the labelled analytes to be separated efficiently according to their molecular size variations with a resolution factor equal to 7.8 and a number of theoretical plates of more than 500 000 per meter. The MCE method was applied to assay BCN and VGN in tablets using 6-aminohexanoic acid as an internal standard. The method sensitivity was enhanced by application of combined stacking and a dynamic pH junction. The method was applied to assay BCN in human plasma and human urine samples with a detection limit lower than 0.3 ng mL−1 and mean extraction recoveries of more than 95% (% RSD < 7) after protein precipitation with methanol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...