A novel sample cell for reducing the “Position Effect” in laser ablation MC-ICP-MS isotopic measurements†
Abstract
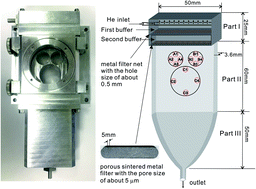
A novel laser ablation cell geometry significantly reduces the so-called position effect on high precision and accuracy isotopic measurements by Laser Ablation-Multiple Collector-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (LA-MC-ICP-MS). The peak shape, amplitude and pulse duration of the 56Fe signal for a single laser shot at the carrier gas flow rate in a range from 0.85 to 1.4 L min−1 were studied, and then twelve analytical areas in the sample cell were selected to assess the homogeneity of aerosol transport efficiency in response to a single laser shot under optimized gas flow conditions. To further investigate whether position effects occur in the new cell, the Fe isotopic composition of Balmat pyrite was measured with extreme separation distances between the ‘sample’ and ‘standard’ in horizontal and vertical carrier gas flow directions in two gas flow rate scenarios. The results show that the position effect on Fe isotopic ratios is obvious at a flow rate of 0.85 L min−1. Nevertheless, the position effect is negligible at a flow rate of 1.00 L min−1. The Fe isotopic composition of in-house reference pyrite sample H1 is determined with δ56Fe and δ57Fe values of −0.11 ± 0.20 (2SD, n = 24) and −0.19 ± 0.40 (2SD, n = 24), respectively. These results are consistent with those measured by MC-ICP-MS solution methods (95% confidence interval). We conclude that the new sample cell can be extensively applied for high precision and accuracy LA-MC-ICP-MS stable isotope analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...