Multi-element analysis of single nanoparticles by ICP-MS using quadrupole and time-of-flight technologies†
Abstract
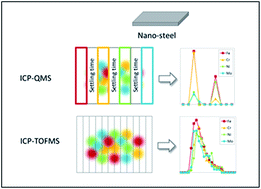
Determining composition, shape, and size of nanoparticles dispersed in a complex matrix is necessary in the assessment of toxicity, for regulatory actions, and environmental monitoring. Many types of nanoparticles that are currently used in consumer products contain more than one metal which are often not uniformly distributed (e.g., core–shell nanoparticles). This compositional and structural complexity makes their characterization difficult. In this study, we investigate the capability of single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (spICP-MS) using time-of-flight (TOF) and quadrupole (Q) mass analyzers to determine the composition, size distribution, and concentration of a series of nanoparticles that are used in a variety of industrial applications: BiVO4, (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 and steel (which contains Fe, Cr, Ni, Mo) nanoparticles. In addition, we tested both types of mass analyzers with Au-core/Ag-shell nanoparticles, which are well-characterized and have already been used for assessment of multi-element capabilities of spICP-MS. The results confirm that both types of mass analyzers produce accurate estimations of the size of Au-core/Ag-shell particles. For other multi-element nanoparticles, spICP-MS provided the size of aggregates and/or agglomerates in the prepared suspensions. In general, particle size detection limits (dLOD) of spICP-TOFMS instruments with values of 29 nm for Ti, 14 nm for Mo, and 7 nm for Au, are smaller than those obtained for the quadrupole instruments. This study finds that only spICP-TOFMS can accurately assess the elemental composition of nano-steel particles. By contrast, spICP-QMS is limited to the detection of 2 elements in an individual particle and the elemental composition of nano-steel particles is less accurate. In general, spICP-TOFMS was able to quantify multiple elements with high precision and that currently makes it the first choice for multi-element detection of unknown nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...