Surface interaction of doxorubicin with anatase determines its photodegradation mechanism: insights into removal of waterborne pharmaceuticals by TiO2 nanoparticles†
Abstract
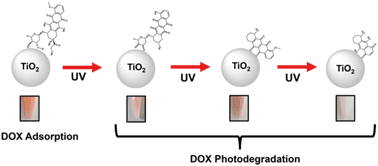
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanomaterials are extensively used in environmental and energy research. However, their utility is governed by surface interactions with surrounding environments and molecules. A deep understanding of these interactions is critical for the development of advanced TiO2 applications. Herein, we systematically investigate the adsorption of doxorubicin (DOX), a highly toxic chemotherapeutic and model antibiotic pharmaceutical, onto anatase TiO2 nanoparticles and correlate the photodegradation mechanism of DOX with its surface adsorption. Compared to the photodegradation of non-adsorbed species in solution by mobile hydroxyl radicals, the adsorption-dependent surface oxidation by UV-induced holes on TiO2 is more efficient. This study underscores the importance of controlling surface adsorption within photodegradation applications via pH alteration, which would be highly relevant for photo-oxidative remediation of environmental organic pollutants with amine or carbonyl functionalities that chemisorb on titania surfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...