Visible-light-driven CO2 photoreduction over ZnxCd1−xS solid solution coupling with tetra(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin iron(iii) chloride†
Abstract
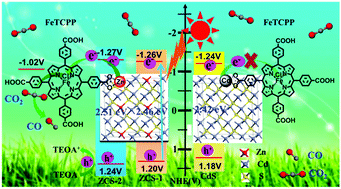
Construction of solid solution semiconductors has attracted much attention in photocatalysis by virtue of their tunable elemental composition and band structure. The integration of semiconductor sensitizers with molecular catalysts provides a promising way to fabricate highly efficient, selective and stable systems for CO2 photoreduction. Here ZnxCd1−xS (ZCS) solid solutions with a well-defined floccule-like morphology composed of nanoribbons are synthesized and used as the photosensitizer to couple with tetra(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin iron(III) chloride (FeTCPP) for CO2 reduction. The effects of changes in surface atoms of the ZCS solid solution on the performance of CO2 photoreduction are investigated. Regardless of the presence of FeTCPP, our results show that the introduction of Zn into CdS can affect the activity and selectivity of CO2 photoreduction, as well as the stability of the obtained photocatalysts. More importantly, the presence of Zn can build efficient electron transfer channels from ZCS to FeTCPP and, thus, greatly facilitate the interfacial charge transfer. Benefitting from the efficient charge separation and electron transfer, ZCS-1/FeTCPP (Zn0.14Cd0.84S/FeTCPP) exhibits the highest activity for CO2 reduction under visible-light irradiation, with a CO yield of 1.28 μmol and a selectivity up to 93% after 4 h.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...