How fine-tuned for energy transfer is the environmental noise produced by proteins around biological chromophores?†
Abstract
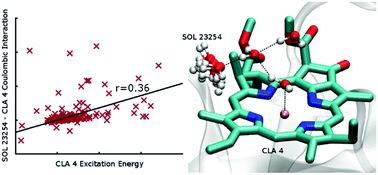
We investigate the role of the local protein environment on the energy transfer processes in biological molecules, excluding from the analysis the effect of intra-chromophore nuclear motions, and focussing on the exciton–phonon coupling. We studied three different proteins (FMO and two variants of the WSCP protein) with different biological functions but similar chromophores, to understand whether a classification of chromophores based on the details of the environment would be possible, and whether specific environments enhance or suppress the coupling between exciton and protein dynamics. Our results show that despite the different biological role, there is no significant difference in the influence of the environment on the properties of the chromophores. Additionally, we show that the main role in influencing molecular properties is played by solvent molecules: the interaction occurs on a medium-range scale, and the solvent is kept in place by a strong H-bond network being free to rotate, suggesting a dipole–dipole interaction mechanism. Steric hindrance exerted by other moieties can help modulating the interactions and tuning the energy transfer process. Overall, considering also the relatively greater importance of intra-molecular nuclear motions, the protein environment around biological chromophores does not appear fine-tuned for a specific function.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...