Plastic deformation and twinning mechanisms in magnesian calcites: a non-equilibrium computer simulation study†
Abstract
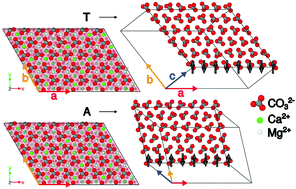
Deformation twinning provides a mechanism for energy dissipation in crystalline structures, with important implications on the mechanical response of carbonate biogenic materials. Carbonate crystals can incorporate magnesium, e.g. in the sea, modifying their elastic response significantly. We present a full atom computational investigation of the dependence of the twinning response of calcite with magnesium content, covering compositions compatible with three main structures, calcite, dolomite and magnesite. We find, in agreement with experiments that the incorporation of magnesium disfavors twinning as a dissipation mechanism in ordered structures (dolomite, magnesite), however the response is strongly dependent on the arrangement of the magnesium ions in the crystal structure. We show that structures with a high content of magnesium (>33%) in a disordered arrangement, lead to plastic response before twinning or fracturing. We demonstrate that the position of the magnesium ions plays a key role in the determination of the crystal deformation mode. This observation is correlated with the formation of percolation clusters of magnesium in magnesian calcites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...