Construction of d10 metal coordination polymers based on in situ formed 3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid from different precursors: influence of in situ hydrolysis reactions on assembly process†
Abstract
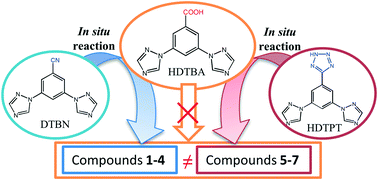
To explore the influence of in situ hydrolysis reaction on the assembly of coordination polymers (CPs), seven new CPs based on in situ formed 3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoic acid (HDTBA) from two different precursors, 3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzonitrile (DTBN) and 5-(3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)-2H-tetrazole (HDTPT), were constructed. When DTBN is used as a precursor, four CPs, namely, [Zn(DTBA)2]n (1), [Cd(DTBA)2]n (2 and 3), and {[Cd(DTBA)2]·H2O}n (4), were obtained under hydrothermal conditions. Compound 1 is a nested double layer structure based on (6,3) networks. Compounds 2 and 3 are supramolecular isomers which were synthesized from Cd(NO3)2·6H2O and Cd(ClO4)2·6H2O, respectively. Compound 2 displays a 3D framework with a two-folded interpenetrating bimodal (3,6)-connected rtl network topology, while compound 3 possesses a 2D network with a CdI2-type network topology. Compound 4 presents a 3D framework that can be denoted as a new (3,5)-connected topological net with point symbol of {4·6·8}{4·64·85}. When HDTPT was used as a precursor under similar conditions, three CPs, namely, Zn(DTBA)NO3]n (5), [Zn(DTBA)Cl]n (6) and {[Cd(DTBA)(NO3)(H2O)]·H2O}n (7), were obtained. Compound 5 is a 2D network with a (4·82) topology, while compounds 6–7 are 2D networks with the same (6,3) network topology. Interestingly, anion⋯π interaction between inorganic anions and triazolyl ring can be observed and plays an important role in connecting the 2D layer into 3D supramolecular frameworks in 5–7. The results show that the in situ hydrolysis reactions affect the assembly processes significantly. The in situ reactions regulate the structure via changing the concentration (but not the total amount) of HDTBA during the assembly process, which in turn regulates the coordination competition between HDTBA and inorganic anions, thus generating different structures. Furthermore, their solid-state fluorescent properties were investigated at room temperature.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...