Synthesis of a superparamagnetic ultrathin FeCO3 nanorods–enzyme bionanohybrid as a novel heterogeneous catalyst†
Abstract
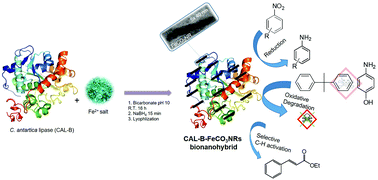
Herein we report a straightforward synthesis of an ultrathin protein-iron(II) carbonate nanorods (FeCO3-NRs) heterogeneous bionanohybrid at room temperature and in aqueous media. The enzyme induced the in situ formation of well-dispersed FeCO3 NRs on a protein network. The addition of NaBH4 as a reducing agent allowed us to obtain nanorods (5 × 40 nm) with superparamagnetic properties. This bionanohybrid showed excellent catalytic results in reduction, oxidation and C–C bond reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...