Increased extracellular matrix density disrupts E-cadherin/β-catenin complex in gastric cancer cells†
Abstract
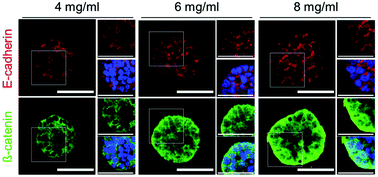
During gastric cancer (GC) progression, increased extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, notably collagen type I, correlates with an overall increase in expression of the mesenchymal phenotype. In GC tissue, the intestinal epithelium exhibits impaired cell–cell adhesion and enhanced cell–ECM adhesion. The alteration of intercellular integrity is one of tumorigenesis feature including tumor invasion and metastasis. Using a density-varying ECM, we studied the effect of ECM density on both intercellular- and ECM-interactions according to alterations of ECM-mediated signaling. A dense collagen matrix increases integrin-mediated cell–ECM interactions with phosphorylated FAK and ERK signaling in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells (AGS, MKN74), which regulates GC proliferation and the chemotherapeutic response. In addition, GC cells exhibited a disrupted membranous E-cadherin/β-catenin complex and, remarkably, showed cytoplasmic or nucleic localization of β-catenin in response to collagen density. Furthermore, we found that membranous E-cadherin/β-catenin complex could be recovered by inhibiting the phosphorylation of FAK, which in turn influences the chemotherapeutic effect. These results provide insight into how matrix density differentially regulates cancer cell phenotype and may have significant implications for the design of biomaterials with appropriate physical properties for in vitro tumor models.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...