An aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for simple and sensitive detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in milk
Abstract
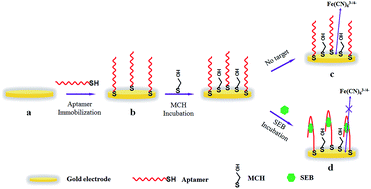
Staphylococcal food poisoning is one of the most commonly encountered foodborne illnesses that results from the consumption of foods containing staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) produced by enterotoxigenic strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Among the SEs, staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) is one of the most commonly presented serotypes in staphylococcal food-poisoning cases, and rapid, accurate, and reliable detection of SEB is necessary and significant to protect public health from SEB. Herein, a label-free and convenient aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for SEB detection was explored. In the absence of SEB, only the aptamer and mercaptohexanol (MCH) assembled on electrode surfaces, resulting in an efficient electron transfer and a small faradaic impedance response of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4−. Upon the addition of SEB, SEB assembled on gold electrode surfaces owing to the high specific recognition and affinity constants of the aptamer and SEB. In this state, the electron transfer of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− was greatly inhibited, due to SEB on gold electrode surfaces which prevents [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− from accessing the electrode surface for efficient electron transfer, and a large faradaic impedance response of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− was obtained. [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− was used as the redox probe to evaluate the interfacial electron transfer resistance of the biosensor, and the change in Ret against the logarithm of SEB concentration was found to be linear over the range from 0.5 ng mL−1 to 500 ng mL−1, with a detection limit of 0.17 ng mL−1 (S/N = 3). In order to demonstrate the applicability and reliability of the proposed method in complex matrices such as milk samples, the results of this assay and the ELISA kit were compared. The relative percentage error between the two methods ranged from −8.38 to 8.33, which indicates that there is no significant difference between the results obtained by the two methods. It also indicates that the proposed method holds great promise for real sample detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...