Dispersion-aggregation-dispersion colorimetric detection for mercury ions based on an assembly of gold nanoparticles and carbon nanodots†
Abstract
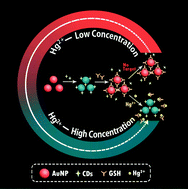
Mercury is a common heavy metal element in natural systems and is highly toxic to the human body. Herein, a novel colorimetric detection of Hg2+ ions is proposed based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) induced by carbon quantum dots (CDs) with the assistance of glutathione (GSH). In this sensing system, the AuNP/CDs composite forms through Au–N bonds. Simultaneously, the color of the solution turns from wine red to blue. The well-dispersed AuNPs can be restored after the addition of GSH, because GSH competes with CDs to bind onto the surface of AuNPs and protect AuNPs from aggregation. In the presence of Hg2+ ions, GSH can chelate with Hg2+ to form a complex, which subsequently enables CDs to facilitate the aggregation of the AuNPs again. Therefore, according to the red-to-blue color change, a colorimetric sensor is established for the sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ with a detection limit of 7.5 nM. Moreover, this sensor is successfully used to detect Hg2+ spiked in environmental water. This very simple and cost-effective strategy will promote the development of a colorimetric sensor for the determination of other metal ions in biological and environmental fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...