A facile graphene oxide-based fluorescent nanosensor for the in situ “turn-on” detection of telomerase activity†
Abstract
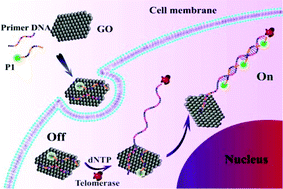
A facile and sensitive method for the quantitative detection of telomerase and in situ imaging of intracellular telomerase is developed by using a graphene oxide (GO)-based fluorescent nanosensor. The nanosensor consists of a fluorescent DNA (P1) adsorbed on the GO surface. Here, GO serves not only as a fluorescence quencher but also as a carrier to successfully transport P1 into cancer cells as a signal reporter. P1 is a dye-labeled single-stranded DNA complementary to the telomeric repeated sequence, and initially the combination of P1 and GO exhibits minimal background fluorescence. When telomerase extends its repeat units of TTAGGG on the 3′-end of the primer-DNA, the fluorescence of P1 is subsequently recovered because the telomeric repeated sequence can hybridize with P1 and liberate it from the GO surface. This method enables the determination of telomerase activity down to 10 cells. For the in situ detection of telomerase, upon endocytosis of the P1/GO combinatorial probe into living cancer cells, the intracellular telomerase extends its primer to produce the telomeric repeated sequence and then turns on the fluorescence of P1, which can be directly monitored by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The feasibility of the assay is further investigated by treating with telomerase-related drugs, and the results demonstrate its potential in antitumor drug screening and cancer therapy evaluation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...