In vitro antibacterial activity of oxide and non-oxide bioceramics for arthroplastic devices: I. In situ time-lapse Raman spectroscopy
Abstract
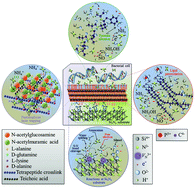
Over the next two decades, a strong demographic demand for arthroplastic devices coupled with a decreased efficacy of antibiotics has been predicted to result in an exponential increase in the number of periprosthetic joint infections (PJIs). Advanced strategies are therefore required to improve the local peri-implant immune response and curb the pathogenic events of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. The use of biomaterials that autonomously counter infections is one approach to improve orthopedic outcomes. Using conventional molecular biology characterization methods and advanced Raman spectroscopy, this study examined the bacteriostatic response of two bioceramic materials commonly employed as prosthetic implants: zirconia-toughened alumina (ZTA) and silicon nitride (Si3N4). Unlike the ZTA, it was found that non-oxide Si3N4 possesses an inherently anti-infective surface chemistry, which acts in a responsive way against bacterial loading. The mechanistic details of its behavior are elucidated. Non-oxide bioceramics appear to be promising, but their full development requires a transitional approach that integrates the fundamental biochemical concepts with clinical outcomes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Clinical spectroscopy


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...