Enhanced piezoluminescence in non-stoichiometric ZnS:Cu microparticle based light emitting elastomers†
Abstract
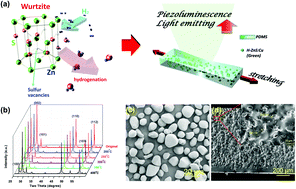
Piezoluminescence (PZL), also referred to as mechanoluminescence (ML), is a promising energy conversion mechanism for realizing mechanically driven photon sources including handheld displays, lighting, bioimaging and sensing applications. However, the realization of a visible PZL intensity at room temperature from low mechanical stresses has been fundamentally challenging. Herein, we describe a PZL elastomer exhibiting significantly enhanced brightness under ambient conditions. The elastomer consisted of defect-engineered non-stoichiometric Cu-doped ZnS (ZnS:Cu) microparticles in a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) matrix. The role of the defect structure was found to be the controlling parameter in the nature of PZL emission. Hydrogenation treatment was designed to induce a controlled concentration of sulfur vacancies that provided the trapped electrons, which had a strong correlation with the PZL performance of ZnS:Cu. An optimum electron concentration was necessary in order to maximize the PZL intensity due to an adequate electron energy transfer ratio between non-radiative recombination (NRR) and thermal radiative recombination (TRR). The light-emitting elastomer with an optimum content of PZL particles maximized the stress-mediated electroluminescence–piezoelectric coupling, enabling visible PZL brightness under indoor light conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...