Structure–property relationships of low sintering temperature scheelite-structured (1 − x)BiVO4–xLaNbO4 microwave dielectric ceramics†
Abstract
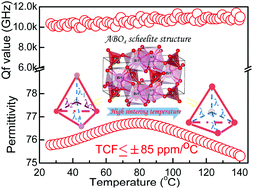
A series of (1 − x)BiVO4–xLaNbO4 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) ceramics were prepared via a solid state reaction method. A scheelite-structured solid solution was formed for x ≤ 0.5 but for x > 0.5, tetragonal scheelite, monoclinic LaNbO4-type and La1/3NbO3 phases co-existed. As x increased from 0 to 0.1, the room temperature crystal structure gradually changed from monoclinic to tetragonal scheelite, associated with a decrease in the ferroelastic phase transition temperature from 255 °C (BiVO4) to room temperature or even below. High sintering temperatures were also found to accelerate this phase transition for compositions with x ≤ 0.08. Temperature independent high quality factor Qf >10 000 GHz in a wide temperature range 25–140 °C and high microwave permittivity εr ∼76.3 ± 0.5 was obtained for the x = 0.06 ceramic sintered at 800 °C. However, small changes in composition resulted in a change in the sign and magnitude of the temperature coefficient of resonant frequency (TCF) due to the proximity of the ferroelastic transition to room temperature. If TCF can be controlled and tuned through zero, then (1 − x)BiVO4–xLaNbO4 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) is a strong candidate for microwave device applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...