Charge separation in an acceptor–donor–acceptor triad material with a lamellar structure†
Abstract
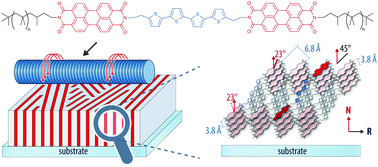
Linking covalently both electron donor and acceptor components is an efficient way to gain thermodynamic control over the formation of well-ordered heterojunction materials suitable for organic photovoltaics. In this context, we attached flexible polymer segments to the termini of a (perylene bisimide)–quaterthiophene–(perylene bisimide) triad. The microphase segregation of the resulting coil-rod-coil architecture served to reliably promote the formation of lamellar phases. The lamellae were oriented vertically relative to the substrate, and they could be laterally aligned by mechanical rubbing, as determined by small and wide angle X-ray scattering, transmission electron microscopy, electron diffraction and AFM. Transient absorption spectroscopy revealed that light absorption was followed by charge separation and that charge recombination was slower in thin films than for solution-phase samples, especially when longer side chains were used. Thus, this study is a first step towards reliable lamellar phase segregation in donor–acceptor materials on the route towards improved materials for organic photovoltaics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...