2,3-Dialdehyde nanofibrillated cellulose as a potential material for the treatment of MRSA infection†
Abstract
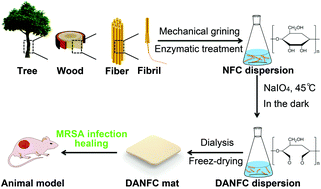
Nanocellulose materials have undergone rapid development in recent years as promising biomedical materials due to their excellent physical and biological properties, in particular their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low cytotoxicity. In this study, we prepared 2,3-dialdehyde nanofibrillated cellulose (DANFC) by sodium periodate oxidation, which is a mild oxidation process. With increasing oxidation time, the antimicrobial activity of DANFC against both Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) improved. DANFC also displays good biocompatibility with mammalian cells, and shows good blood compatibility. In addition, animal studies and histology results reveal that DANFC can accelerate wound healing and enhance the formation of blood vessels and epithelium.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...