Dual responsive hydrogels based on functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an injectable platform for tumor therapy and tissue regeneration†
Abstract
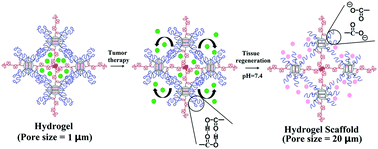
To achieve effective tumor therapy and regenerate new tissue from defects formed by tumor atrophy, a dual responsive hydrogel integrating the stepwise delivery of anti-tumor drugs/growth factors and pH/thermo induced structural transformation is developed, based on polymer (poly N-isopropylacrylamide (PNIPAM) and polyacrylic acid (PAA)) functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs). Due to the thermally responsive tangle between PNIPAM chains and the pH triggered hydrogen bonds in PAA chains, these injectable MSNs would immediately switch from nanoparticles to compact hydrogels in a tumor environment (37.5 °C, pH 6.8), where the concentrated network structure in the hydrogel is in charge of the loading and local delivery of anti-tumor drugs. The MSNs serve as nanocarriers for growth factors, which are localized by crosslinked networks. The sustained release of growth factors only occurred with the cleavage of hydrogen bonds in PAA chains, which is triggered by the pH increase to 7.4 after the cure of the tumor. Moreover, the hydrogen bond cleavage would also cause the swelling of the hydrogel, which not only fills the defects but generates plenty of cell-level pores, resulting in an excellent scaffold for attachment and proliferation of healthy cells. Therefore, the dual responsive MSN-hydrogels offer a promising strategy for sequential tumor therapy and tissue regeneration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...