A redox-responsive strategy using mesoporous silica nanoparticles for co-delivery of siRNA and doxorubicin†
Abstract
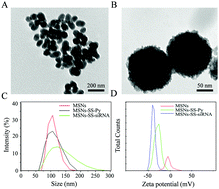
Co-delivery of gene and drug therapies for cancer treatment remains a major goal of nanocarrier research. In this study, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) were used to co-deliver siRNA and doxorubicin (Dox) for redox-controlled release. The present nanocarrier (MSNs-SS-siRNA@Dox) has mesoporous silica cores that can be loaded with Dox, while siRNA connects to the core surface by disulfide linkage and plays a gatekeeper role. Disulfide linkages were also utilized to target intracellular GSH, and their cleavage led to the release of Dox and siRNA. Release of siRNA and Dox was correlated with GSH concentrations, and rapid release at 10 mM GSH reflected reductive cleavage of intermediate disulfide linkages. Subsequent experiments using an in vitro Dox delivery and release assay indicated that MSNs-SS-siRNA@Dox significantly enhanced the accumulation of Dox in cells compared with that after treatment with free Dox. Moreover, MSNs-SS-siRNA@Dox has sufficient efficiency to knock down target protein expression. More importantly, MSNs-SS-siRNA@Dox displayed great potential for tumor targeting and achieved satisfactory therapeutic effects on tumor growth inhibition in vivo. In summary, the present nanoparticles may provide an effective strategy for the design and development of controlled release and co-delivery of siRNA and drugs for cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...