In situ reduction of silver nanoparticles on hybrid polydopamine–copper phosphate nanoflowers with enhanced antimicrobial activity
Abstract
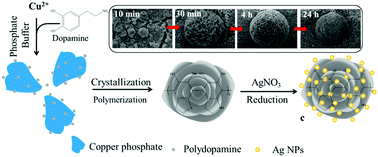
The development of novel antimicrobial materials with high antimicrobial activity and low environmental impact is of importance for global health, but has proven to be challenging. Herein we report a facile mineralization process to create a flower-like, porous antimicrobial agent, which is stable, selective, effective and environmentally benign. This new antimicrobial material is made of organic polydopamine (PD) and inorganic (copper phosphate) components, where the incorporation of PD on the hybrid architecture endows the direct in situ reduction of silver ions into silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) without the need of external toxic reductants. The combination of Ag NPs and high surface area of the nanoflower results in high selectivity in the antimicrobial activity towards Gram-negative Escherichia coli (E. coli), while leaving co-cultured mammalian cells healthy and intact. Moreover, we show that the hybrid antimicrobial material is stable, and can be easily recovered after use, avoiding the persistent hazard to the environment. We envision that this novel antimicrobial agent may find useful applications for clinical studies and industrial products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...