Synergic effect of Bi, Sb and Te for the increased stability of bulk alloying anodes for sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
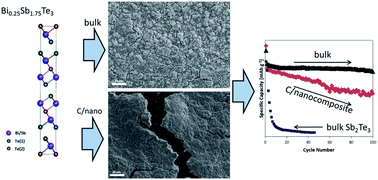
Effective use of materials that undergo alloying reactions with sodium is hampered by the substantial volume changes that occur during cycling. One of the most common approaches to improve cycling stability is nanostructuring. However, the processes required for material's particle downsizing are hardly transferable to large scale production. To alleviate such problems, the ternary alloy Bi0.25Sb1.75Te3 has been designed and its electrochemical performance investigated. The choice of system was driven by the large reversible capacities displayed by both Sb and Te coupled with the highly desirable fracture resistance of Bi. Indeed, micron-sized bulk powder of Bi0.25Sb1.75Te3 showed high capacity retention (retaining 91% of the initial capacity after 100 cycles at 200 mA g−1) and an excellent average coulombic efficiency (99.9% for 100 cycles), both of which are superior to those observed for the bi-component counterpart Sb2Te3 as bulk and nanosized forms. This behaviour indicates that a small substitution of Sb with Bi does have profound effects on the electrochemical performance. Even more compelling is the observation that enhanced performance and stability are observed when the active material is in the form of micron-sized powder and not when nanosized in a carbon composite. This behaviour is ascribed to the influence of particle size on the (de)sodiation reaction pathways and on the thickness and composition of the SEI passivation layer. The improved stability of the ternary alloy shows that careful optimization of multicomponent systems could lead to remarkable performance enhancement without the necessity of size confinement, opening the way to facile and low-cost electrode manufacturing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...