Synthesis and characterization of novel stellate sea-urchin-like silver particles with extremely low density and superhydrophobicity†
Abstract
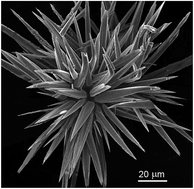
Stellate sea-urchin-like silver particles with 24 to 56 rays of 30–50 μm in length have been synthesized by chemical reduction of silver nitrate aqueous solution by thiocarbamide alkaline solution. The synthesis was carried out under solar irradiation at room temperature. The stellate Ag particles are hydrophobic; their relative density is smaller than that of water. By varying the pH and the ratio between the concentrations of reagents, it is possible to produce fine-dispersed silver powders and films from stellate particles with different ray lengths.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...