A chemically bonded NaTi2(PO4)3/rGO microsphere composite as a high-rate insertion anode for sodium-ion capacitors†
Abstract
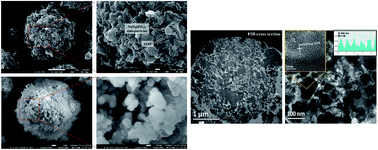
We report on the synthesis of a high rate NaTi2(PO4)3/graphene composite for use as an anode material for high power Na-ion hybrid capacitors with the following characteristics; (1) reduction of the particle size of NaTi2(PO4)3 to the nanometer scale in order to reduce the Na+ ion diffusion length, (2) chemical bonding between NaTi2(PO4)3 nanoparticles and graphene in order to improve electrical conductivity, and (3) interconnected nanoporous structures in order to allow easy access of Na+ ions to NaTi2(PO4)3. For this, the NaTi2(PO4)3/rGO microsphere composite was prepared via a facile spray drying method using a solution mixture of graphene oxide, NaH2PO4·2H2O, Ti(OC2H5)4 and NH4H2(PO4)3, in which all the components of the titanium were present as ionic species in order to facilitate the chemical bonding between NaTi2(PO4)3 and rGO in the composite. The NaTi2(PO4)3/rGO microsphere composite had a Ti–O–C bond between NaTi2(PO4)3 nanoparticles (<80 nm) and rGO and interconnected nanoporous structures. The NaTi2(PO4)3/rGO microsphere composite exhibited a near theoretical specific capacity of 133 mA h g−1 at a 0.1 C-rate and excellent rate capability (70% capacity retention at a 50 C-rate) with very stable cycling performance (only 2% capacity loss after 200 cycles at a high rate of 10C). Furthermore, the energy density and power density of the NHC assembled with a NaTi2(PO4)3/rGO anode and an AC-based cathode are far better than those of other NHCs assembled using other metal oxide-based anodes and AC cathodes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...