Study of the electrooxidation of borohydride on a directly formed CoB/Ni-foam electrode and its application in membraneless direct borohydride fuel cells†
Abstract
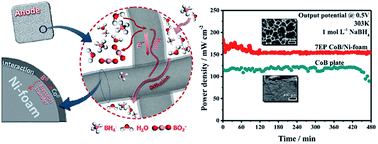
As a promising energy source, direct borohydride fuel cells (DBFCs) have attracted a lot of attention. Since the electrooxidation of BH4− always accompanies the hydrolysis reaction, the energy density of DBFCs is closely related to the composition and structure of the anode. The formation of hydrogen formed by the hydrolysis of BH4− and the high exothermic nature of the reaction, as well as the strong basicity of the fuel, bring strict demands for the stability of the anode. Consequently, the designation and fabrication of an ideal anode are effective routes to enhance the performance of DBFCs. By comprehensive consideration of convenience, the electric/thermal conductivity of the electrode, the diffusion of the reactants/products and the effective cost, the electroless plating method was adopted and a CoB anode was directly formed on a Ni-foam substrate. The anode showed high electrocatalytic activities from electrooxidation of NaBH4 with a low CoB loading amount. Especially, the anode showed distinct stability compared to the CoB plate prepared by the pressed method and the catalytic activity could retain 65% after an accelerated life time test of 500 cyclic voltammetry cycles, which was due to the strong interactions between the CoB particles and Ni-foam substrate. Among all the investigated anodes, the CoB/Ni-foam electroless anode deposited for 7 times showed the best performance. It was applied in a membraneless DBFC which showed a maximum power density of 230 mW cm−2 in 1 mol L−1 NaBH4 + 3 mol L−1 NaOH at 313 K. These characteristics allowed the electroless plating CoB/Ni-foam catalyst to exhibit enormous potential as an anode for practical applications in DBFCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...