Microwave-synthesized tin oxide nanocrystals for low-temperature solution-processed planar junction organo-halide perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
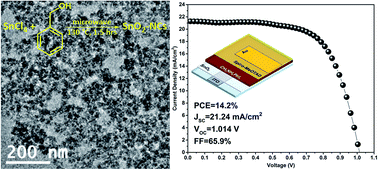
Tin oxide has been demonstrated to possess outstanding optoelectronic properties such as optical transparency and high electron mobility; therefore, it was successfully utilized as an electron transporting layer in various kinds of solar cells. In this study, for the first time, highly dispersible SnO2 nanoparticles were synthesized by a microwave-assisted non-aqueous sol–gel route in an organic medium. Ethanol dispersion of the as-prepared nanoparticles was used to cast a uniform thin layer of SnO2 without the aid of an aggregating agent and at low temperatures. Organohalide perovskite solar cells were fabricated using SnO2 as the electron transporting layer. Morphological and spectroscopic investigations, in addition to the good photoconversion efficiency obtained, evidenced that the nanoparticles synthesized by this route have optimal properties such as small size and crystallinity to form a continuous film. Furthermore, this method allows high reproducibility and scalability of the film deposition process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...