Combatting AMR: photoactivatable ruthenium(ii)-isoniazid complex exhibits rapid selective antimycobacterial activity†
Abstract
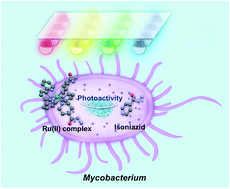
The novel photoactive ruthenium(II) complex cis-[Ru(bpy)2(INH)2][PF6]2 (1·2PF6, INH = isoniazid) was designed to incorporate the anti-tuberculosis drug, isoniazid, that could be released from the Ru(II) cage by photoactivation with visible light. In aqueous solution, 1 rapidly released two equivalents of isoniazid and formed the photoproduct cis-[Ru(bpy)2(H2O)2]2+ upon irradiation with 465 nm blue light. We screened for activity against bacteria containing the three major classes of cell envelope: Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis, Gram-negative Escherichia coli, and Mycobacterium smegmatis in vitro using blue and multi-colored LED multi-well arrays. Complex 1 is inactive in the dark, but when photoactivated is 5.5× more potent towards M. smegmatis compared to the clinical drug isoniazid alone. Complementary pump-probe spectroscopy measurements along with density functional theory calculations reveal that the mono-aqua product is formed in <500 ps, likely facilitated by a 3MC state. Importantly, complex 1 is highly selective in killing mycobacteria versus normal human cells, towards which it is relatively non-toxic. This work suggests that photoactivatable prodrugs such as 1 are potentially powerful new agents in combatting the global problem of antibiotic resistance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...