Highly uniform Fe3O4 nanoparticle–rGO composites as anode materials for high performance lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
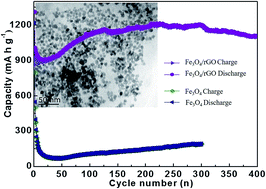
Current lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) based on carbonaceous anodes are close to their theoretical performance limits and can hardly meet the demand for high energy applications. Anode materials based on transition metal oxides are promising alternatives to graphite, stemming from their high lithium storage capacity. Among them, iron oxides have the advantages of rich raw materials, low prices, and high theoretical capacities. Herein, we report a facile strategy of improving the capacity and cycling stability of LIBs via the use of reduced graphene oxide-doped Fe3O4 nanoparticles (around 6.45 nm) as anode materials. Galvanostatic cycling measurements show that cells with Fe3O4/rGO nanocomposites deliver a reversible specific capacity of 1108 mA h g−1 at a current density of 0.5 A g−1 even after 400 cycles. The unique structure of Fe3O4/rGO nanocomposites is responsible for the high cycling performance. The rGO component enables high electrical conductivity while the homogeneous distribution of nano-sized Fe3O4 in rGO favors the diffusion and charge transfer of ions. The void space amongst the nanoparticles and the rGO nanosheets can accommodate volume expansion during cycling. This novel tactic can be used in the preparation of other transition metal oxides with ultra-small and uniform nanoparticles such as SnO2, Co2O3, TiO2 and RuO2 for high-energy LIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...