Nanoparticle cellular uptake by dendritic wedge peptides: achieving single peptide facilitated delivery†
Abstract
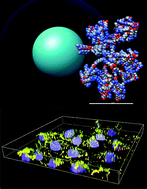
Significant efforts are being undertaken to optimize the cargo carrying capacity and especially the cellular delivery efficiency of functionalized nanoparticles for applications in biological research and pharmacological delivery. One approach to increasing nanoparticle surface cargo display capacity is to decrease the number of moieties required for mediating cellular delivery by improving their efficiency. We describe a series of multivalent cell penetrating peptide (CPP) dendrimers that facilitate rapid cellular delivery of prototypical nanoparticle-semiconductor quantum dots (QDs). The modular CPP dendrimers were assembled through an innovative convergent oxime ligation strategy between (Arg9)n motifs and a dendritic QD-coordination scaffold. Dendrimeric peptides sequentially incorporate a terminal (His)6 motif for metal-affinity QD coordination, a Pro9 spacer, a branching poly-lysine scaffold, and wedged display of (Arg9)n binding motifs with n = 1×, 2×, 4×, 8×, 16× multivalency. QD dendrimer display capacity was estimated using structural simulations and QD–(Arg9)1–16 conjugates characterized by dynamic light scattering along with surface plasmon resonance-based binding assays to heparan sulfate proteoglycan surfaces. Cellular uptake via endocytosis was confirmed and peptide delivery kinetics investigated as a function of QD–(Arg9)1–16 conjugate exposure time and QD assembly ratio where cellular viability assays reflected no overt cytotoxicity. The ability of single dendrimer conjugates to facilitate cellular uptake was confirmed for QD–(Arg9)2–16 repeats along with the ability to deliver >850 kDa of protein cargo per QD. Minimizing the number of CPPs required for cellular uptake is critical for expanding nanoparticle cargo carrying capacity and can allow for inclusion of additional sensors, therapeutics and contrast agents on their surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...