Modulatory effects of arginine, glutamine and branched-chain amino acids on heat shock proteins, immunity and antioxidant response in exercised rats
Abstract
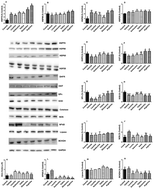
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are endogenous proteins whose function is to maintain the cell's tolerance to insult, and glutamine supplementation is known to increase HSP expression during intense exercise. Since few studies have addressed the possibility that supplementation with other amino acids could have similar effects to that of glutamine, our objective was to evaluate the effects of leucine, valine, isoleucine and arginine as potential stimulators of HSPs 25, 60, 70 and 90 in rats subjected to acute exercise as a stressing factor. The immune markers, antioxidant system, blood parameters, glycogen and amino acid profile responses were also assessed. Male Wistar rats were divided into seven groups: control (rest, without gavage), vehicle (water), L-leucine, L-isoleucine, L-valine, L-arginine and L-glutamine. Except for the control, all animals were exercised and received every amino acid by oral gavage. Arginine supplementation up-regulated muscle HSP70 and HSP90 and serum HSP70, however, none of the amino acids affected the HSP25. All amino acids increased exercise-induced HSP60 expression, except for valine. Antioxidant enzymes were reduced by exercise, but both glutamine and arginine restored glutathione peroxidase, while isoleucine and valine restored superoxide dismutase. Exercise reduced monocyte, platelet, lymphocyte and erythrocyte levels, while leucine stimulated immune response, preserved the levels of the lymphocytes and increased leukocytes and maintained platelets at control levels. Plasma and muscle amino acid profiles showed specific metabolic features. The data suggest that the tissue-protecting effects of arginine could proceed by enhancing specific HSPs in the body.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...