Li2TiSiO5: a low potential and large capacity Ti-based anode material for Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
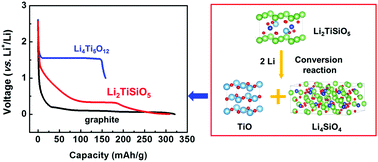
To date, anode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been dominated by carbonaceous materials, which have a low intercalation potential but easily allow lithium dendrites to form under high current density, leading to a safety risk. The other anode material, the “zero-strain” spinel-structured Li4Ti5O12, with a ∼1.5 V vs. Li+/Li intercalation potential, exhibits excellent cycling stability and avoids the issues of dendrite growth and Li plating. The low capacity and high voltage of Li4Ti5O12, however, result in low energy density. Herein, we report a new and environmentally friendly anode material, Li2TiSiO5, which delivers a capacity as high as 308 mA h g−1, with a working potential of 0.28 V vs. Li+/Li, and excellent cycling stability. The lithium-storage mechanism of this material is also proposed based on the combination of in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, neutron powder diffraction with Fourier density mapping, ex situ X-ray absorption near edge structure analysis, ex situ transmission electron microscopy, and density-functional theory calculations with the projector-augmented-wave formalism. The lithium-storage mechanism of this material is shown to involve a two-electron (Ti4+/Ti2+ redox) conversion reaction between TiO and Li4SiO4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...