Enhanced photo-responsiveness in a photoswitchable system model: emergent hormetic catalysis†
Abstract
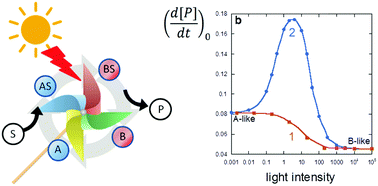
Michaelis Menten catalysis by a T-photochromic system has been analyzed numerically. Using an appropriate set of rate constants and quantum yields, we have evidenced an enhanced photo-responsiveness at a medium light intensity: the plot of the initial rate vs. light intensity is bell-shaped. This emergent phenomenon can be qualified as hormetic catalysis. The analysis of the chemical flows shows that a directional rotation occurs within the cyclic scheme. Non equilibrium conditions are provided by two independent sources: the chemical energy dissipation from the irreversible exergonic reaction and the steady transformation of light into heat by T-photochromism. A literature survey, showing that most of the required kinetic features are not so rare, let us anticipate its practical feasibility.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...