De-orphaning the marine natural product (±)-marinopyrrole A by computational target prediction and biochemical validation
Abstract
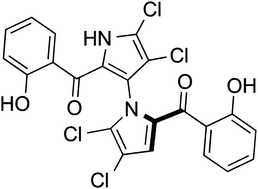
Exploring the full potential of bioactive natural products and phenotypic screening hits for drug discovery and design requires profound understanding of the macromolecular targets involved. We present a computational method for target prediction, and showcase its practical applicability, taking the marine anticancer compound (±)-marinopyrrole A as an example. With an overall accuracy of 67%, the ligand-based method employed identified the natural product as a potent glucocorticoid, cholecystokinin, and orexin receptor antagonist. The results of this study demonstrate the utility of fast computational target assessment for medicinal chemistry and chemical biology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...