Electrochemical manipulation of cell populations supported by biodegradable polymeric nanosheets for cell transplantation therapy†
Abstract
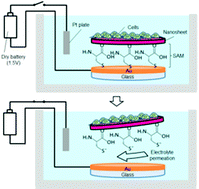
We describe an electrochemical method of harvesting cells cultured on a biodegradable polymeric nanosheet (cell/nanosheet construct), which is stabilized on a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of thiol molecules. A poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanosheet was attached by hydrophobic interactions onto the surface of a SAM of L-cysteine coated onto a gold electrode. Retinal pigment epithelial cell lines (RPE-J cells) were cultured on the nanosheet to form a monolayer. An AA-size dry battery was used to apply a negative electrical potential, causing reductive desorption of the SAM from the gold surface. Within one minute of application of the voltage, the cell/nanosheet of several mm in diameter was successfully detached without the loss of cell viability in a gentle stream of the electrolyte solution. The use of a porous electrode shortened the detachment time due to the more efficient permeation of the electrolyte solution to the electrode surface. Cell transplantation following the harvesting process was demonstrated by the local delivery of RPE-J cell/nanosheet constructs into the subretinal space of rat eyes through a capillary needle. This nanosheet-based approach that allows the on-demand harvesting of cell/nanosheet constructs and their subsequent transplantation in a minimally-invasive manner could play an important role in cell transplantation therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...