The combination of NIR spectroscopy and HPLC chromatography for differentiating lotus seed cultivars and quantitative prediction of four main constituents in lotus with the aid of chemometrics
Abstract
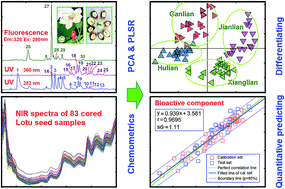
Lotus has been widely cultivated and consumed in Asia, Oceania and America, and it is not only used as an ornamental plant but also as a dietary staple. In this work, fingerprinting techniques based on NIR spectroscopy and HPLC chromatography were used to discriminate four important kinds of lotus seed cultivars, Xianglian, Jianlian, Ganlian and Hulian. By the use of the NIR spectra and the aid of genetic algorithm-partial least squares (GA-PLS) and principal component analysis (PCA), cored lotus seed samples were successfully discriminated into four cultivars. High performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) characteristic peaks detected at different wavelengths can also be used for PCA analysis to differentiate the lotus seed cultivars. Furthermore, quantitative prediction analysis of total sugar, total polysaccharide, liensinine and rutin in cored lotus seed (liensinine and rutin are mainly in lotus plumule) can be successfully performed with the use of the combined data matrix of 30 common characteristic HPLC peaks and 37 GA-PLS selected NIR spectral variables (wavelengths). The results suggested that the combination of NIR and HPLC supported by chemometrics is suitable for the discrimination of the plant cultivars and quantitative prediction of the active constituents in lotus seed samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...