Beneficial protective effects of 2-allyl amino 4-methyl sulfanyl butyric acid on glucose metabolism and glycoprotein components in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats with molecular modeling
Abstract
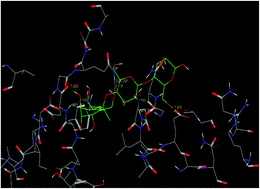
In the present study, the potential effects of 2-allyl amino 4-methyl sulfanyl butyric acid (AMSB) on the glucose metabolism and glycoprotein components in streptozotocin (STZ) induced experimental diabetic rats were determined. Further, molecular modeling was performed to investigate the modes of AMSB interaction with insulin receptor active sites. The blood glucose and plasma insulin levels were measured in the STZ induced diabetic rats, whereas the glucose metabolism and glycoprotein components were analyzed from the plasma and tissues. After oral treatment of AMSB there was a significant reduction in blood glucose, glucose-6-phosphatase, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and glycogen phosphorylase. On the other hand, the activity of the glycoprotein levels, such as hexose, hexosamine, fucose and sialic acid, were significantly reduced. In addition, a significant elevation in plasma insulin, hexokinase, glycogen and glycogen synthase were also observed in the AMSB treated rats. The molecular modeling study revealed that AMSB has a stable binding pattern to the active site of insulin, with a Gscore value of −7.34 Kcal mol−1. From this study we conclude that AMSB has a potent antidiabetic activity in addition to its protective effect on glycoprotein metabolism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...