Synthesis and size dependent magnetostrictive response of ferrite nanoparticles and their application in magnetoelectric polymer-based multiferroic sensors
Abstract
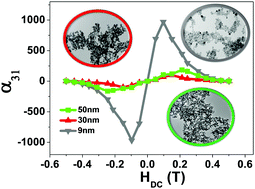
This work shows that it is possible to synthesize, chemically tailor and optimize the magnetostriction of ferrite nanoparticles and improve the magnetoelectric (ME) response of their multiferroic composites. Thus, Fe3O4 nanoparticles with different sizes have been synthesized by a solvothermal procedure and an oxidative hydrolysis method. The first method results in nanoparticles with 9 nm average size and 167 ppm magnetostriction; the second one in nanoparticles with average sizes of 30 nm and 50 nm and magnetostriction of 17 ppm and 26 ppm, respectively. Furthermore, Fe3O4/P(VDF-TrFE) multiferroic nanocomposites were produced with those nanoparticles, showing ME voltage coefficients (α31) of 920 μV cm−1 Oe−1, 100 μV cm−1 Oe−1 and 150 μV cm−1 Oe−1, respectively, for samples fabricated with nanoparticles with 9 nm, 30 nm and 50 nm average size. The high magnetostrictive response and the biocompatibility of ferrite nanoparticles, together with their anhysteretic magnetic response, enhance their application potential for biomedical applications as well as their use in high performance ME materials for sensors and actuators.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...