A novel synthesis of carbon nanotubes directly from an indecomposable solid carbon source for electrochemical applications†
Abstract
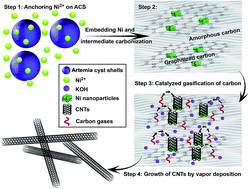
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are synthesized through a novel low cost self-vaporized chemical vapor deposition (SCVD) technique from an indecomposable solid carbon source for the first time. This method was manipulated to avoid the injection of flammable gasses, by producing gaseous carbon (e.g. CO) through an in situ catalyzed gasification of the intermediate product induced by KOH. Simultaneously, the as-produced gaseous carbons will deposit onto the pre-imbedded Ni nanocatalyst surface and form CNTs. The growth mechanism is discussed in detail by adjusting the KOH amount. The as-prepared CNTs are rich in oxygen and deficiencies, which endow them with abundant active sites for electrochemical applications. Superior supercapacitor performance is achieved with a specific capacitance 6 times higher than that of commercial CNTs. This technique represents a novel, convenient approach toward large scale production of CNTs directly from a solid carbon precursor, and would show promising applications in various industrial fields.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...