Easily accessible conjugated pyrene sulfonates as cathode interfacial materials for polymer solar cells†
Abstract
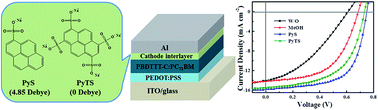
Two easily accessible π-conjugated pyrene sulfonates, 1-pyrenesulfonic acid sodium salt (PyS) and 1,3,6,8-pyrenetetrasulfonic acid tetrasodium salt (PyTS), as cathode interfacial layers (CILs) for polymer solar cells (PSCs) are demonstrated. The two interlayer materials, with polar sulfonates directly linking to a conjugated unit, are quite different from other kinds of interfacial materials with functional groups attached to non-conjugated alkyl chains. Moreover, the two molecules show distinct intramolecular dipoles. PyS with a strong permanent dipole moment can reduce the work function of the bulk-heterojunction (BHJ) films, while centrosymmetric PyTS with no overall dipole has little effect on the work function of BHJ films. It is also found that PyS based devices show much improved charge transport ability and conductivity than those based on PyTS. As a result, PyS based devices exhibit a high power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 7.46% for the PBDTTT-C:PC71BM system, while PyTS based devices show a relatively low PCE of 6.28%. A higher efficiency of 8.82% is achieved for PTB7-Th as the donor. In addition, benefitting from the planar structure of the pyrene units, PyS with high conductivity can function efficiently in a wide thickness range of 2 to 41 nm.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...