Niobium carbide nanofibers as a versatile precursor for high power supercapacitor and high energy battery electrodes†
Abstract
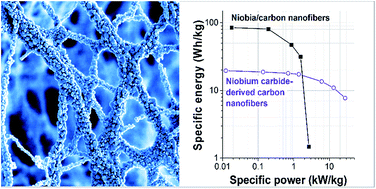
This study presents electrospun niobium carbide/carbon (NbC/C) hybrid nanofibers, with an average diameter of 69 ± 30 nm, as a facile precursor to derive either highly nanoporous niobium carbide-derived carbon (NbC–CDC) fibers for supercapacitor applications or niobium pentoxide/carbon (Nb2O5/C) hybrid fibers for battery-like energy storage. In all cases, the electrodes consist of binder-free and free-standing nanofiber mats that can be used without further conductive additives. Chlorine gas treatment conformally transforms NbC nanofiber mats into NbC–CDC fibers with a specific surface area of 1508 m2 g−1. These nanofibers show a maximum specific energy of 19.5 W h kg−1 at low power and 7.6 W h kg−1 at a high specific power of 30 kW kg−1 in an organic electrolyte. CO2 treatment transforms NbC into T-Nb2O5/C hybrid nanofiber mats that provide a maximum capacity of 156 mA h g−1. The presence of graphitic carbon in the hybrid nanofibers enabled high power handling, maintaining 50% of the initial energy storage capacity at a high rate of 10 A g−1 (64 C-rate). When benchmarked for an asymmetric full-cell, a maximum specific energy of 86 W h kg−1 was obtained. The high specific power for both systems, NbC–CDC and T-Nb2O5/C, resulted from the excellent charge propagation in the continuous nanofiber network and the high graphitization of the carbon structure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...