Ni@NiO core/shell dendrites for ultra-long cycle life electrochemical energy storage†
Abstract
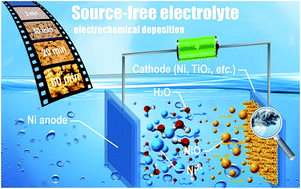
A dendritic Ni@NiO core/shell electrode (DNE) is successfully fabricated by electrodeposition in a Ni-free electrolyte, with a Ni anode providing Ni ions through dissolution and diffusion. The unique structure is ideal for electrochemical energy storage since the dendrites provide a large surface area for easy electrolyte infiltration; the metal core improves the electrode conductivity with a shortened ion diffusion path, and the metal oxide shell is active for faradaic charge storage. As a result, the synthesized DNE demonstrates a high specific capacitance of 1930 F g−1 and a high areal capacitance of 1.35 F cm−2, with super-long cycle stability. The gravimetric capacitance of the DNE hardly shows any decay after 70 000 cycles at a scan rate of 100 mV s−1. It was also demonstrated that our electrodeposition method in a source-free electrolyte is universal to deposit dendritic Ni-compounds on many other types of substrates, versatile for different applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...