Engineered superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for ultra-enhanced uranium separation and sensing†
Abstract
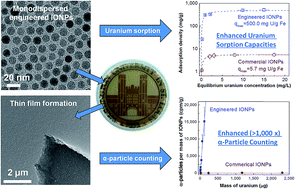
Rapid separation and analysis of radionuclides in the environment remains a challenge despite broad needs, particularly for ultra-sensitive field detection. Ionizing radiation detection/counting can be limited by sample matrix shielding and long integration times, while more sensitive spectrometry requires extensive sample preparation and advanced instrumentation. In this work we have designed, synthesized, and demonstrated optimized iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) for low-energy, high-efficiency separation and concentration for ultra low-level uranium (as a model actinide) sensing in dilute (environmental) applications. Monodispersed single crystalline, IONPs with an ordered, oleic acid bilayer coating, are demonstrated to bind ca. 50% wt U/wt Fe, under optimal conditions, which is the highest reported for any iron-based sorbent materials to date. Superparamagnetic material properties allow for subsequent low-field magnetic separations from heterogeneous and relatively large (dilute) aqueous volumes resulting in highly concentrated residues. Through a final filtration step, high particle (aqueous) stability gives rise to self-assembling, homogenous, sub-micron films, arranged to minimize α-particle self-shielding, thus allowing for optimized sensitivity/detection with a handheld Gieger counter. Taken together, we demonstrate a ca. 10 000-fold increase in uranium detection sensitivity when compared to commercially available nanoscale IONPs (combining sorption and detection/counting enhancements). Lastly, these advantages are demonstrated for real world samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...