Triconstituent co-assembly synthesis of N,S-doped carbon–silica nanospheres with smooth and rough surfaces†
Abstract
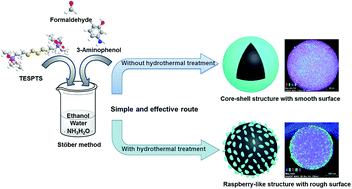
Multifunctional porous nanospheres are desirable for many applications, but their synthesis involves multi-step procedures and their simplification still remains a challenge. Herein, we demonstrate a facile synthesis of polymer–silica nanospheres by using an extended Stöber method via triconstituent co-assembly of 3-aminophenol, formaldehyde, and bis[3-(triethoxysilyl)propyl]tetrasulfide followed by copolymerization. N,S-doped carbon–silica nanospheres with either smooth or rough surface can be obtained by direct carbonization of the polymer–silica nanospheres. The carbon–silica spheres feature multifunctional properties and exhibit very good performance as adsorbents for CO2 capture (67 cm3 g−1 at 0 ± 1 °C and 1.0 bar) and as supercapacitor electrodes with high specific capacitance (221 F g−1). This strategy could pave the way for design of carbon nanostructures at molecular level for multi-purpose applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...