N-cadherin-functionalized polymer-tethered multi-bilayer: a cell surface-mimicking substrate to probe cellular mechanosensitivity
Abstract
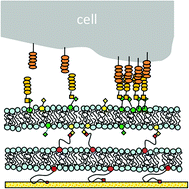
Fate and function of anchorage-dependent cells depend on a variety of environmental cues, including those of mechanical nature. Previous progress in the understanding of cellular mechanosensitivity has been closely linked to the availability of artificial cell substrates of adjustable viscoelasticity, allowing for a direct correlation between substrate stiffness and cell response. Exemplary, polymeric gel substrates with polymer-conjugated cell-substrate linkers provided valuable insight into the role of mechanical signals during cell migration in an extracellular matrix environment. In contrast, less is known about the role of external mechanical signals across cell–cell interfaces, in part, due to the limitations of traditional polymeric substrates to mimic the remarkable dynamics of cell–cell linkages. To overcome this shortcoming, we introduce a cell surface-mimicking cell substrate of adjustable stiffness, which is comprised of a polymer-tethered lipid multi-bilayer stack with N-cadherin linkers. Unlike traditional polymeric cell substrates with polymer-conjugated linkers, this novel artificial cell substrate is able to replicate the dynamic assembly/disassembly of cadherin linkers into linker clusters and the long-range movements of cadherin-based cell-substrate linkages observed at cell–cell interfaces. Moreover, substrate stiffness can be changed by adjusting the number of bilayers in the multi-bilayer stack, thus enabling the analysis of cellular mechanosensitivity in the presence of artificial cell–cell linkages. The presented biomembrane-mimicking cell substrate provides a valuable tool to explore the functional role of mechanical cues from neighboring cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...